ar valence electrons|6.4 Electronic Structure of Atoms (Electron Configurations) : Pilipinas Valence electrons are the electrons in the highest occupied principal energy level of an atom. In the second period elements, the two electrons in the \(1s\) sublevel are called inner-shell electrons and are not involved directly in the element's reactivity, or in the . 안녕하세요. (주)이담 입니다.. 저희 실적을 소개하는 글에서도 '입면도', '투시도', '평면도'라는 용어들을 자주 보셨을텐데요,
PH0 · What Are Valence Electrons? Definition and Periodic Table
PH1 · Valence electrons (video)
PH2 · Valence electron
PH3 · Valence Electrons Chart for All Elements
PH4 · How to Find the Valence Electrons for Argon (Ar)?
PH5 · How Many Valence Electrons Does Argon (Ar) Have?
PH6 · Determine valence electrons using the periodic table
PH7 · 6.4 Electronic Structure of Atoms (Electron Configurations)
PH8 · 3.1: Valence Electrons
PH9 · 3.10: Valence Electrons
PH10 · 2.9: Valence Electrons
The Hamtramck Water Department provides water for about 22,413 residents living in the Hamtramck area, Michigan. Established in 1922, the Hamtramck Water Department collects surface water from the Detroit River, situated within the Lake St. Clair, Clinton River, Detroit River, Rouge River, Ecorse River in the U.S. and parts of the Thames .Login to OneDrive with your Microsoft or Office 365 account.
ar valence electrons*******Valence electrons are the electrons in the highest occupied principal energy level of an atom. In the second period elements, the two electrons in the \(1s\) sublevel are called inner-shell electrons and are not involved directly in the element's reactivity, or in the .Valence electrons are the outer-shell electrons of an atom. Valence electrons .6.4 Electronic Structure of Atoms (Electron Configurations)Valence electrons are the electrons in the highest occupied principal energy level .ar valence electrons Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell, or energy level, of an atom. For example, oxygen has six valence electrons, two in the 2 s subshell and four in the 2 p subshell. We can write the configuration of oxygen's valence electrons as 2 . Mar 23, 2023 Learn what valence electrons are and how to find them for different elements. See examples of valence electrons for main group and transition metals and the difference between valence and oxidation state.The electrons that determine valence – how an atom reacts chemically – are those with the highest energy. For a main-group element, the valence electrons are defined as those electrons residing in the electronic shell of highest principal quantum number n. Thus, the number of valence electrons that it may have depends on the electron configuration in a simple way. For example, the electronic c.
Valence electrons are the outer-shell electrons of an atom. Valence electrons determine the reactivity of an atom. Atoms have a tendency to have eight . Valence electrons are the electrons in the highest occupied principal energy level of an atom. In the second period elements, the two electrons in the 1s 1 s sublevel .Learn how to determine the number of valence electrons for an element using the periodic table. An atom's valence electrons are the electrons in its outermost shell. In the .ar valence electrons 6.4 Electronic Structure of Atoms (Electron Configurations)For example, gallium (Ga, atomic number 31) has the electron configuration [Ar]4s 2 3d 10 4p 1, which contains three valence electrons (underlined). The completely filled d . The total number of electrons in the last shell after the electron configuration of argon is called the valence electrons of argon. The last shell of argon has eight . You may assume the valences of the chemical elements—the number of electrons with which an atom will bond or form—are those that can be derived by looking at the groups (columns) of the periodic table. While these are the most common valences, the real behavior of electrons is less simple.
Solution. Element A is located in Period 2, the 5th position in 2p-block.Before the electrons are placed in 2p subshell, the 2s subshell must be filled first. This means that A has two valence electrons in 2s (2s 2) and five valence electrons in 2p (2p 5).Answer: 2s 2 2p 5. It has 2 + 5 = 7 valence electrons.. Element B is located in Period 3, the 2nd .
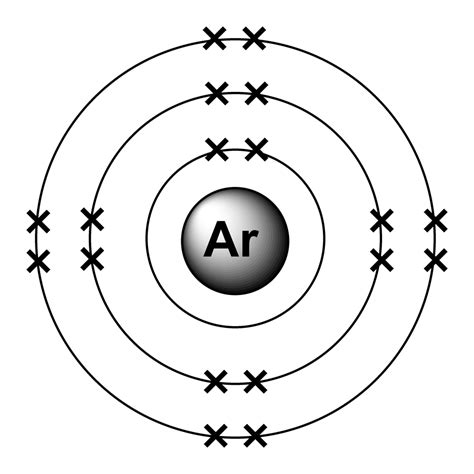
Argon holds 18 electrons in its outer shell with the electron configuration of 2,8,8. So, this is why Argon has no need to either gain or lose the electrons. The eight electrons fill the valence shell to bring about the 0 valencies of Argon. Check here for Argon Valence Electrons or Argon Valency (Ar) with Dot Diagram here.

Bohr diagrams indicate how many electrons fill each principal shell. Group 18 elements (helium, neon, and argon are shown in Figure 2) have a full outer, or valence, shell. A full valence shell is the most stable electron configuration. Elements in other groups have partially filled valence shells and gain or lose electrons to achieve a stable .In order to write the Argon electron configuration we first need to know the number of electrons for the Ar atom (there are 18 electrons). When we write the configuration we'll put all 18 electrons in orbitals around the nucleus of the Argon atom. In writing the electron configuration for Argon the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital.
2. Find the electron configuration for the element you are examining. Once you know an element's electron configuration, finding its number of valence electrons is quite simple (except, of course, for the transition metals.) If you're given the configuration from the get-go, you can skip to the next step. There are two ways to find the number of valence electrons in Argon (Ar). The first is to use the Periodic Table to figure out how many electrons Argon has i.
Generally, valence electrons can participate in the formation of chemical bonding, but core electrons cannot. While core electrons are not involved in bonding, they influence the chemical reactivity of an atom. The electron configuration of a oxygen atom is. O: 1s22s22p4 (1.9B.1) (1.9B.1) O: 1 s 2 2 s 2 2 p 4. which may be shorted.
The traditional island groups of Luzon, the Visayas, and Mindanao are composed of eight (Regions I, II, III, IV-A, and V, and CAR, NCR, and Mimaropa), four (VI, VII, VIII, and NIR), and six (IX, X, XI, XII, . Western Mindanao (renamed as Zamboanga Peninsula, still designated as Region IX) Central Mindanao (now mostly Soccsksargen, .
ar valence electrons|6.4 Electronic Structure of Atoms (Electron Configurations)